VNC
VNC (Virtual Network Connection) allows you to run graphically intensive applications directly on a remote machine rather than trying to forward an Xsession back to your local host. VNC clients are available for Mac, Windows, and Linux. CGD is using TigerVNC for both the server and clients.
For Apple Mac users, the instllation kit is in Self Service.
Systems available for VNC
- thorodin.cgd.ucar.edu
- tungsten.cgd.ucar.edu
Using VNC
On the remote host
Once you've installed a VNC client on your local host, connect to one of our general use servers. For this example we're using thorodin.cgd.ucar.edu
- SSH to the server
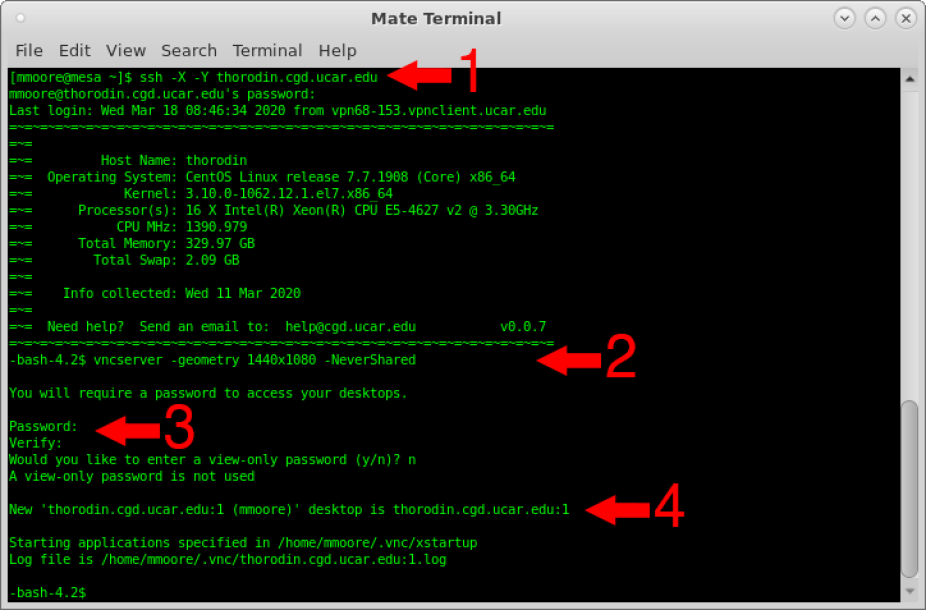
ssh -X -Y thorodin.cgd.ucar.edu - Launch the VNC server
vncserver - Set your vncpasswd if prompted. Make note of the new desktop, it will be something like "thorodin.cgd.ucar.edu:1" Leave your ssh session running, you'll need it when you're finished.
On the local host
Start TigerVNC on your local system and connect to the server.
Enter the full hostname, a colon, and the port number as depicted in item 4 of the image above.
In this case, thorodin.cgd.ucar.edu:1 but your case may vary depending on the server used in item 1 of the image above.
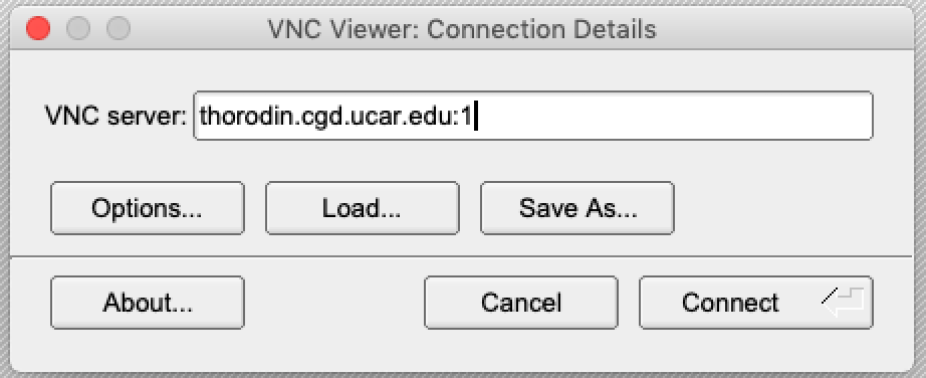
Enter your VNC password
Now you have a remote graphical connection to thorodin. Run your application such as Matlab or IDL. The virtual desktop can be resized by dragging the corners.
VNC sessions are killed daily at 2:00am local time. If you need to runs jobs longer, create them as usual with 'screen' or 'nohup'.